On Thursday, Microsoft unveiled a new suite of features for its AI assistant, marking a step forward by embedding artificial intelligence into one of its flagship products. This initiative, termed Copilot Mode in Microsoft’s Edge browser, seeks to carve a space in the emerging category of AI browsers. Unlike traditional extensions, this innovation provides an intelligent, adaptive AI assistant designed to assist users throughout their web browsing experience.
In a statement, Mustafa Suleyman, CEO of Microsoft AI, elaborated on this vision. He described Copilot Mode in Edge as evolving into an AI browser that acts as a “dynamic, intelligent companion” for users. With user approval, Copilot can observe and analyze open tabs, summarize and compare information, and even perform tasks like booking hotels or completing forms.
Originally launched in July, Edge’s Copilot Mode debuted with fundamental features such as a search bar on new tabs and voice navigation. Initially, the mode was optional and didn't garner the expected attention. However, during Thursday's announcement, Microsoft showcased additional features like “Actions,” enabling form-filling and hotel booking, and “Journeys,” which helps users follow connections across open tabs. These improvements reposition the AI browser concept at the forefront of Microsoft's presentation.
This development follows closely after OpenAI's introduction of the Atlas browser just two days prior. Though Copilot's release timetable has been set for weeks, and its development likely spans months, the resemblance between these two tech innovations is striking.
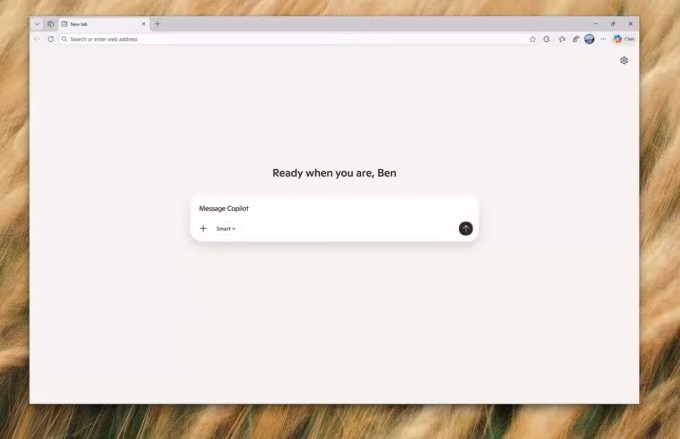
Image Credits: Microsoft (screenshot)
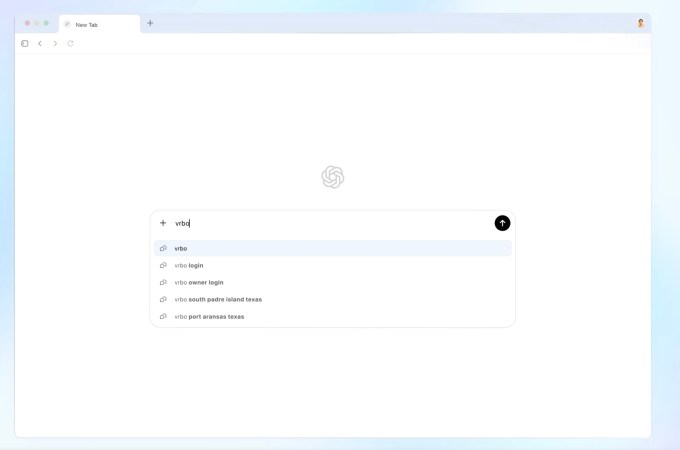
Image Credits: OpenAI (screenshot)
The images depicting the two products highlight their similarities. Microsoft's Copilot uses a slightly darker theme, textual indicators instead of a logo, and employs Windows-style buttons for closing and minimizing, contrasting with MacOS's style. Additionally, Copilot opts for a new tab to feature its AI assistant instead of using a split-screen display. Despite these minor differences, the core functionalities are quite alike.
This resemblance can be attributed to the functional needs of maintaining clean browser aesthetics and the limited options for integrating a chatbot into the “new tab” screen layout. However, the essential distinction lies in the AI models powering each browser, suggesting that superficial similarities may not be significant for users.
While browsers frequently share visual elements, the timing of these releases highlights the competitive dynamics in the AI field, with both companies unveiling similar products in quick succession.
